Projects
Utility Assessment, Master Plan and EIS for the National Institutes of Health Animal Center (NIHAC), Dickerson, MD
A challenging Master Plan for a rural campus that developed organically as purpose built disconnected buildings were constructed over time.
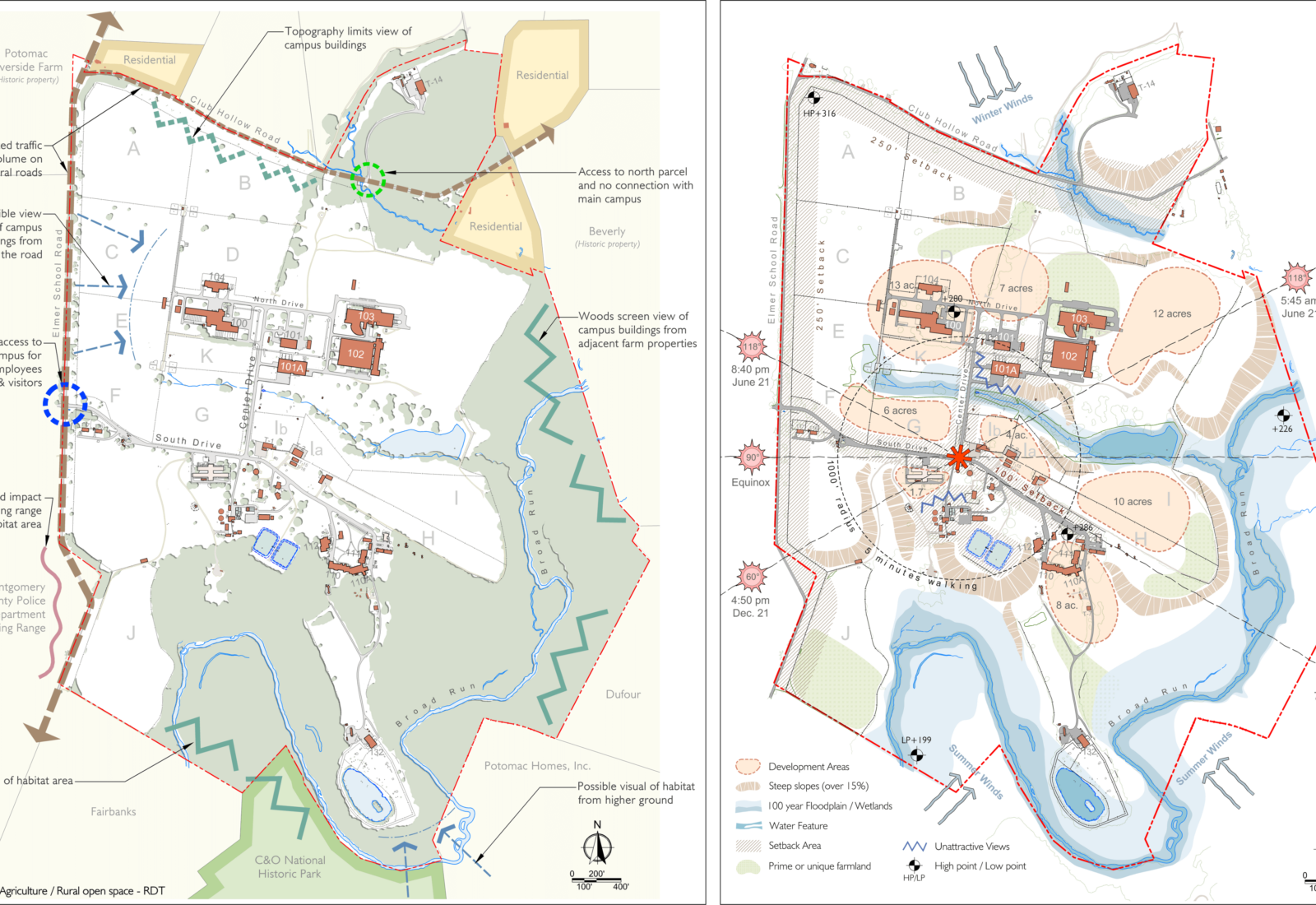
The NIH Animal Center (NIHAC) campus consists of 37 buildings on 513 acres. It serves primarily as an animal care facility for NIH Bethesda’s research activities but also houses some research functions for a few institutes.
The core concept for the Master Plan was the consolidation of facilities for behavioral research and centralized animal holding facilities on the north campus, creating opportunities for collaboration, resource sharing, and easy pedestrian connections.
The project scope included: A) Update and Assessment of the Existing Utilities Infrastructure; and B) Master Plan and Environmental Impact
Study. Assessment tasks included: benchmarking similar facilities; survey/mapping of topography, surface and subsurface features, and utilities; analysis of systems— steam, chilled water, electric power, fuel systems, water, sanitary sewer and data and telecommunications. Modeled systems included steam, chilled water, potable and non-potable water, and sanitary sewers.
The Master Plan tasks included: background research, program requirements, planning goal/vision, environment assessment, opportunities and constraints, development & evaluation of concepts, design guidelines, and an implementation plan. An Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) was developed.
The Plan was subjected to multiple reviews including by the National Capital Planning Commission (NCPC).